ROS 2 Navigation#
Support Limitations
ROS 2 Navigation with Isaac Sim is fully supported on Linux. On Windows, ROS 2 Navigation with Isaac Sim is partially supported and could potentially produce errors.
Learning Objectives#
This ROS2 sample demonstrates NVIDIA Isaac Sim integrated with ROS2 Nav2.
Getting Started#
Prerequisite
You must source your ROS 2 installation from the terminal before running Isaac Sim.
The Nav2 project is required to run this sample. To install Nav2 refer to the Nav2 installation page.
Enable the
isaacsim.ros2.bridgeExtension in the Extension Manager window by navigating to Window > Extensions.This tutorial requires
carter_navigation,iw_hub_navigation, andisaac_ros_navigation_goalROS2 packages, which are provided as part of your NVIDIA Isaac Sim download. These ROS2 packages are located inside the appropriateros2_ws. They contain the required launch file, navigation parameters, and robot model. Complete ROS 2 Installation (Default), make sure the ROS 2 workspace environment is setup correctly.
Note
In Windows 10 or 11, depending on your machine’s configuration, RViz2 might not open properly.
Nav2 Setup#
This block diagram shows the ROS2 messages required for Nav2:

The following topics and message types being published to Nav2 in this scenario are:
ROS2 Topic
ROS2 Message Type
/tf
tf2_msgs/TFMessage
/odom
nav_msgs/Odometry
/map
nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid
/point_cloud
sensor_msgs/PointCloud
/scan
sensor_msgs/LaserScan (published by an external pointcloud_to_laserscan node)
Occupancy Map#
In this scenario, an occupancy map is required. For this sample, you are generating an occupancy map of the warehouse environment using the Occupancy Map Generator extension within NVIDIA Isaac Sim.
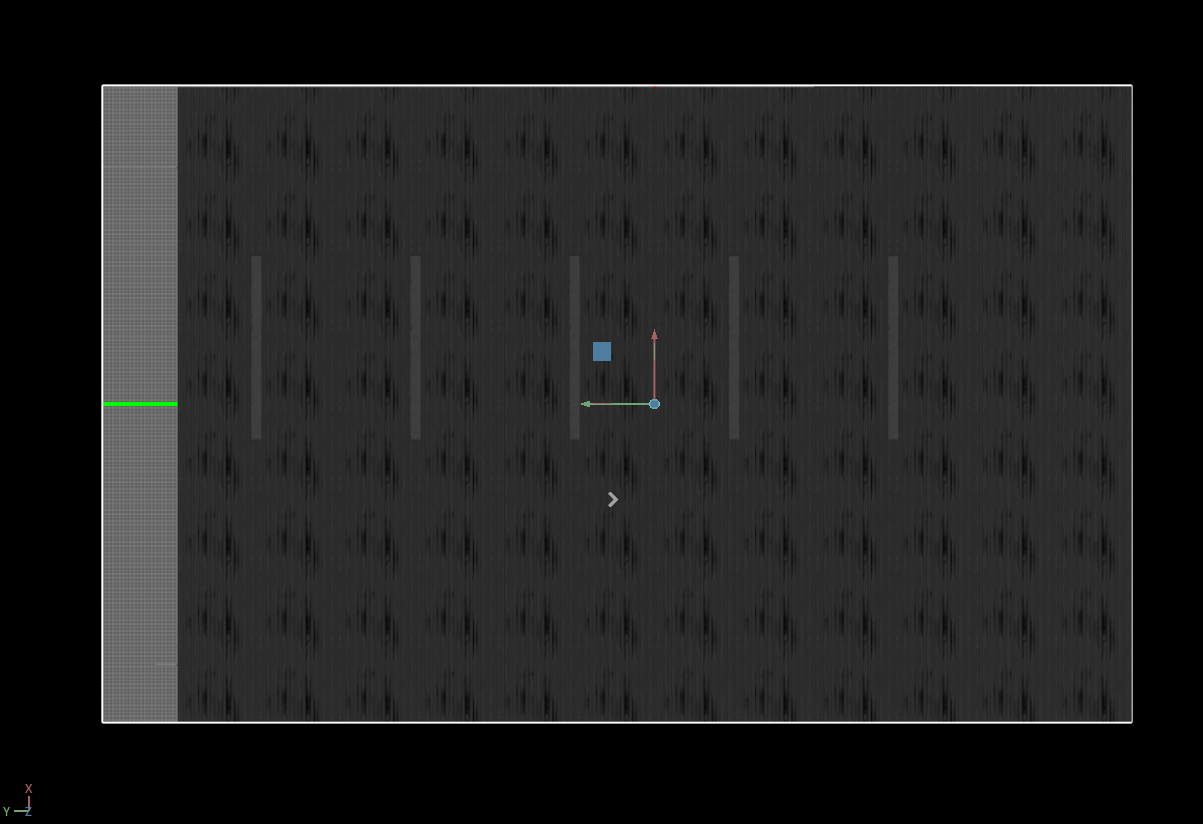
Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples. Click on the Robotics Examples tab. Expand the sections on the left hand side. Open the example: ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter to load the warehouse scenario with the Nova Carter robot.
At the upper left corner of the viewport, click on Camera. Select Top from the dropdown menu.
Go to Tools > Robotics > Occupancy Map.
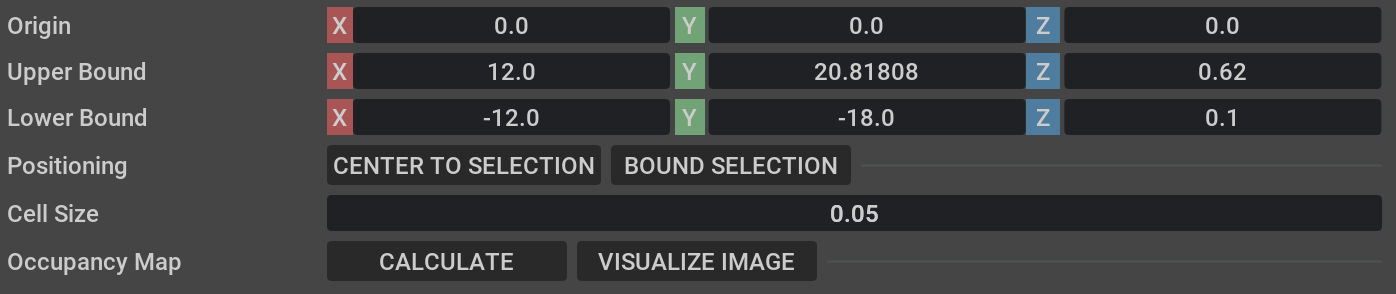
In the Occupancy Map extension, ensure the Origin is set to
X: 0.0, Y: 0.0, Z: 0.0. For the lower bound, setZ: 0.1. For the Upper Bound, setZ: 0.62. Keep in mind, the upper bound Z distance has been set to 0.62 meters to match the vertical distance of the Lidar onboard Nova Carter with respect to the ground.Select the
warehouse_with_forkliftsprim in the stage. In the Occupancy Map extension, click on BOUND SELECTION. Verify that the bounds of the occupancy map are updated to incorporate the selected warehouse_with_forklifts prim. Verify that the map parameters now look similar to the following:Delete the
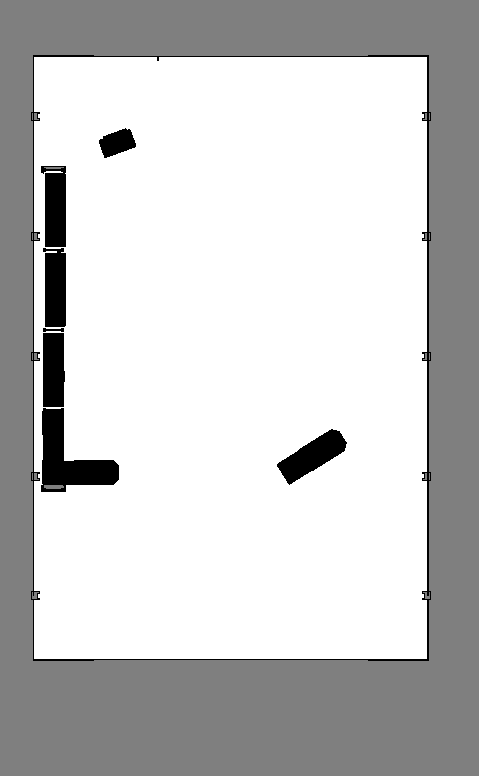
Nova_Carter_ROSprim from the stage.After the setup is complete, click on CALCULATE followed by VISUALIZE IMAGE. A Visualization popup will appear.
For Rotate Image, select 180 degrees and for Coordinate Type select ROS Occupancy Map Parameters File (YAML). Click RE-GENERATE IMAGE. The ROS camera and Isaac Sim camera have different coordinates.
Occupancy map parameters formatted to YAML appear in the field below. Copy the full text.
Create a YAML file for the occupancy map parameters called
carter_warehouse_navigation.yamland place it in themapsdirectory, which is located in the samplecarter_navigationROS2 package (<ros2_ws>/src/navigation/carter_navigation/maps/carter_warehouse_navigation.yaml).Insert the previously copied text in the
carter_warehouse_navigation.yamlfile.Back in the visualization tab in NVIDIA Isaac Sim, click Save Image. Name the image as
carter_warehouse_navigation.pngand choose to save it in the same directory as the map parameters file.
An occupancy map is now ready to be used with Nav2.
Running Nav2#
Nav2 with Nova Carter in a Small Warehouse#
Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples, and then click on the Robotics Examples tab and expand the sections on the left hand side and open the example: ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter to load the warehouse scenario with the Nova Carter robot.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2.
ros2 launch carter_navigation carter_navigation.launch.py
RViz2 opens and begins loading the occupancy map. If a map does not appear, repeat the previous step.
Because the position of the robot is defined in the parameter file
carter_navigation_params.yaml, verify that the robot is already be properly localized. If required, the 2D Pose Estimate button can be used to re-set the position of the robot.Click on the Navigation2 Goal button and then click and drag at the desired location point in the map. Nav2 now generates a trajectory and the robot starts moving towards its destination.
Note
The Carter robot uses the RTX Lidar by default. You can add people assets into the scene and they will be detected by the Lidar when being passed to Nav2.
Some of the ROS2 Image publisher pipelines in the Hawk cameras are disabled by default to improve performance. To start publishing images, open the
_hawkaction graphs found under the robot prim and enable the_camera_render_productnodes. Verify that the ROS Camera publisher nodes, which are downstream of the render product nodes, are enabled by default and that they start publishing when the render product node is enabled. All sensors and images in Nova Carter are being published with Sensor Data QoS. If you want to visualize the images in RViz, expand the image tab, navigate to Topic > Reliability Policy and change the policy to Best Effort.If you notice issues with localizing the robot in open spaces, this is a known issue likely attributed to lower performance. To improve localization, try adding more objects into the scene to introduce more features.
If you notice warnings as shown below, you can disregard them because they are harmless.
[Warning] [omni.graph.core.plugin] /World/Nova_Carter_ROS/differential_drive/differential_controller_01: [/World/Nova_Carter_ROS/differential_drive] invalid dt 0.000000, cannot check for acceleration limits, skipping current step
Nav2 with Nova Carter with Robot Description in a Small Warehouse#
In addition to the previous steps, you can visualize the robot description in the simulation.
Install the nova_carter_description package. Follow the steps Installing the Nova Carter Description Package section.
Launch the Nova Carter description using the launch file that is already provided as part of Isaac Sim Workspaces. This launch file depends on nova_carter_description package being in the system.
ros2 launch carter_navigation nova_carter_description_isaac_sim.launch.py
Open the navigation scene in Isaac Sim. Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples, and then click on the Robotics Examples tab and expand the sections on the left hand side and open the example:
ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter to load the warehouse scenario with the Nova Carter robot.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2.
ros2 launch carter_navigation carter_navigation.launch.py
RViz2 opens and begins loading the occupancy map. If a map does not appear, repeat the previous step.
Verify that the robot model is automatically loaded in the scene in Rviz.
Nav2 with Nova Carter with robot_state_publisher in a Small Warehouse#
The previous Nova Carter warehouse scene had the robot publish transforms (TFs) directly from Isaac Sim. As your robot and scene assets becomes more complex, it will be more scalable and performant to publish static TFs of the robot using the default ROS 2 robot_state_publisher package instead. This way, the robot state publisher will parse the robot URDF and publish the static TFs. Meanwhile, Isaac Sim will be responsible for publishing joint states for moving joints. The robot state publisher will then receive these joint states and convert them to corresponding transforms, adding them to the overall TF tree.
A new Nova Carter robot asset called Nova_Carter_Joint_States_ROS.usd has been created. This asset differs from the original Nova_Carter_ROS.usd in the following ways:
The
transform_tree_odometryaction graph has been removed and an odometry action graph has been added in its place. This effectively removed most TF publishers, only keeping one Raw TF publisher required for the ground truth localization transform (odom frame > base_link frame).New joint_states action graph is added, which publishes the movable joint states for Nova Carter. This will be read in by the robot_state_publisher and it will publish the relevant TFs accordingly.
All hawk camera action graphs have been modified to include a new static TF publisher to add a sub TF tree for the left and right camera frames from each camera mount frame.
Note
Each camera has its own static TF publisher for the following reason: Due to the camera calibration process, the spacing between left and right cameras can differ from device to device. Therefore, the (mount > left camera) and (mount > right camera) transforms are left out of the main URDF and are up to the device driver to provide instead. In this case Isaac Sim acts as the hardware device driver and publishes these static transforms accordingly.
Install the nova_carter_description package. Follow the steps Installing the Nova Carter Description Package section.
In Isaac Sim, open the navigation scene. Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples, and then click on the Robotics Examples tab and expand the sections on the left hand side and open the example: ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter Joint States to load the warehouse scenario with the Nova Carter robot asset with joint state publishers.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to start publishing the robot description using the robot_state_publisher and the official Nova Carter URDF.
ros2 launch carter_navigation nova_carter_description_isaac_sim.launch.py
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2.
ros2 launch carter_navigation carter_navigation.launch.py
Notice the robot model is automatically loaded in the scene in Rviz and performing the same as non-joint state example.
Installing the Nova Carter Description Package#
Note
This section is only supported in Linux for ROS 2 Humble.
The Nova Carter description package contains the robot geometry including meshes that can be used to visualize the robot in RViz2. Follow the steps below to configure this description package for Isaac Sim workflows:
Open a new ROS-sourced terminal. Set up the locale:
locale # check for UTF-8 sudo apt update && sudo apt install locales sudo locale-gen en_US en_US.UTF-8 sudo update-locale LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 LANG=en_US.UTF-8 export LANG=en_US.UTF-8 locale # verify settings
Install the required dependencies.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install gnupg wget sudo apt install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository universe
Register NVIDIA’s GPG Key and Repository.
wget -qO - https://isaac.download.nvidia.com/isaac-ros/repos.key | sudo apt-key add - grep -qxF "deb https://isaac.download.nvidia.com/isaac-ros/release-3 $(lsb_release -cs) release-3.0" /etc/apt/sources.list || \ echo "deb https://isaac.download.nvidia.com/isaac-ros/release-3 $(lsb_release -cs) release-3.0" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list sudo apt-get update
wget -qO - https://isaac.download.nvidia.cn/isaac-ros/repos.key | sudo apt-key add - grep -qxF "deb https://isaac.download.nvidia.cn/isaac-ros/release-3 $(lsb_release -cs) release-3.0" /etc/apt/sources.list || \ echo "deb https://isaac.download.nvidia.cn/isaac-ros/release-3 $(lsb_release -cs) release-3.0" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list sudo apt-get update
Install the nova_carter_description package.
sudo apt install ros-humble-nova-carter-description
Nav2 with iw.hub in Warehouse#
Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples, and then click on the Robotics Examples tab and expand the sections on the left hand side and open the example: ROS2 > Navigation > iw_hub to load the warehouse scenario with the iw.hub robot.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2. The map for the different warehouse environment has already been generated.
ros2 launch iw_hub_navigation iw_hub_navigation.launch.py
RViz2 opens and begins loading the occupancy map. If a map does not appear, repeat the previous step.
Because the position of the robot is defined in the parameter file
iw_hub_navigation_params.yaml, verify that the robot is already be properly localized. If required, the 2D Pose Estimate button can be used to re-set the position of the robot.Click on the Navigation2 Goal button and then click and drag at the desired location point in the map. Nav2 now generates a trajectory and the robot starts moving towards its destination. Verify that the robot avoids dynamic obstacles, such the pallets that are in scene but are not included in the initial map.
Sending Goals Programmatically#
Note
The isaac_ros_navigation_goal package is fully supported on Linux. On Windows, running this package might produce errors.
The isaac_ros_navigation_goal ROS2 package can be used to set goal poses for the robot using a Python node. It is able to randomly generate and send goal poses to Nav2. It is also able to send user-defined goal poses if needed.
Make any changes to the parameters defined in the launch file found under
isaac_ros_navigation_goal/launchas required. Make sure to re-build and source the package and workspace after modifying its contents.The parameters are described below:
goal_generator_type: Type of the goal generator. Use
RandomGoalGeneratorto randomly generate goals or useGoalReaderfor sending user-defined goals in a specific order.map_yaml_path: The path to the occupancy map parameters YAML file. An example file is present at
isaac_ros_navigation_goal/assets/carter_warehouse_navigation.yaml. The map image is being used to identify the obstacles in the vicinity of a generated pose. Required if the goal generator type is set asRandomGoalGenerator.iteration_count: Number of times goal is to be set.
action_server_name: Name of the action server.
obstacle_search_distance_in_meters: Distance in meters in which a generated pose is free from obstacles of any kind.
goal_text_file_path: The path to the text file which contains user-defined static goals. Each line in the file has a single goal pose in the following format:
pose.x pose.y orientation.x orientation.y orientation.z orientation.w. A sample file is present at:isaac_ros_navigation_goal/assets/goals.txt. Required if goal generator type is set asGoalReader.initial_pose: If initial_pose is set, it will be published to the /initialpose topic and goal poses will be sent to action server after that. Format is
[pose.x, pose.y, pose.z, orientation.x, orientation.y, orientation.z, orientation.w].
Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples, and then click on the Robotics Examples tab and expand the sections on the left hand side and open the example: ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter to load the warehouse scenario.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2.
ros2 launch carter_navigation carter_navigation.launch.py
RViz2 opens and begins loading the occupancy map. If a map does not appear, repeat the previous step.
Run the
isaac_ros_navigation_goallaunch file, to start sending goals automatically:ros2 launch isaac_ros_navigation_goal isaac_ros_navigation_goal.launch.py
Note
After any of the following conditions are met, the package stops processing (setting goals):
Number of goals published till now >= iteration_count.
If the
GoalReaderparameter is used and if all the goals from the config file are published.A goal is rejected by the action server.
In rare cases, a very dense map can cause
RandomGoalGeneratorto generate invalid poses. The package will stop processing if the number of invalid poses generated byRandomGoalGeneratorexceeds the maximum number of iteration.
To automatically launch Isaac Sim and Nav2, while programmatically sending navigation goals from a single launch process, refer to Launch Isaac Sim with Nav2.
To learn more about programmatically sending navigation goals to multiple robots simultaneously refer to Sending Goals Programmatically for Multiple Robots.
Sending Goals Using ActionGraph#
Important
Make sure Nav2 is installed and source your ROS2 installation from the terminal before running Isaac Sim. Currently, the following section will not work with internal libraries.
Go to Window > Examples > Robotics Examples to open Robotics Examples tab.
Go to Robotics Examples > ROS2 > Navigation > Nova Carter and click on Load Sample Scene button to load the warehouse scenario with the Nova Carter robot.
Go to Robotics Examples > ROS2 > Navigation > Add Waypoint Follower to open the waypoint follower parameter window.
Make changes to the waypoint follower parameters as required.
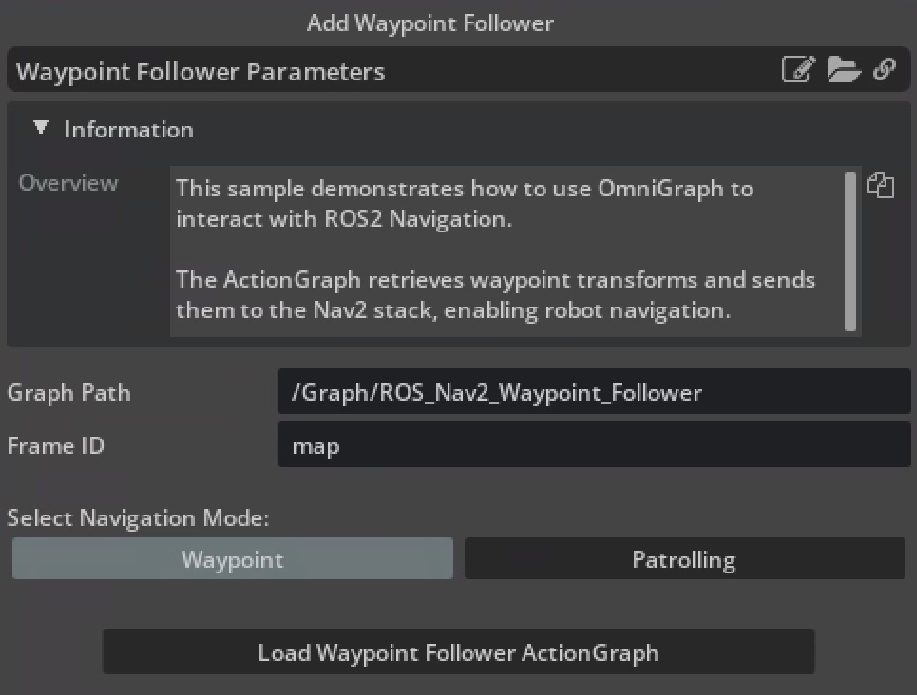
The parameters are described below:
Graph Path: Specify the path within the stage.
Frame ID: Specify the reference frame for navigation tasks.
- Navigation Modes:
Waypoint Mode: Creates a single waypoint to send as a navigation goal. The robot will navigate towards this waypoint.
Patrolling Mode: Creates multiple waypoints (between 2 to 50 inclusive) for continuous patrolling. The robot will navigate between these predefined waypoints continuously.
Waypoint Count: Number of waypoints to generate for Patrolling.
Click on Load Waypoint Follower ActionGraph to create waypoints and add the action graph at Graph Path in stage pane.
Click on Play to begin simulation.
In a new terminal, run the ROS2 launch file to begin Nav2.
ros2 launch carter_navigation carter_navigation.launch.py
RViz2 opens and begins loading the occupancy map. If a map does not appear, repeat the previous step.
Because the position of the robot is defined in the parameter file
carter_navigation_params.yaml, verify that the robot is properly localized. If required, the 2D Pose Estimate button can be used to re-set the position of the robot.Running navigation modes:
- Waypoint:
Adjust the waypoint (/World/Waypoints/waypoint_1) in xy plane of the scene to set the desired goal location.
Open the ROS_Nav2_Waypoint_Follower graph from the stage and click on Send Impulse in the OnImpulseEvent node.
Verify that the robot starts navigating towards the specified goal.
Repeat these steps after each goal is completed to set new waypoint.
- Patrolling:
Adjust the waypoints (/World/Waypoints/waypoint_n) in xy plane of the scene to define the patrol path.
Open the ROS_Nav2_Waypoint_Follower graph from the stage and click on Send Impulse in the OnImpulseEvent node.
Verify that the robot starts patrolling along the set waypoints.
Note
This tutorial uses the AMCL localizer and the action graph is fully supported for this localizer.
If you notice errors as shown below after deleting the graph, you can disregard them because they are harmless. To prevent these logs you can click the “reload node” button to clean up the script nodes before deleting the graph.
2024-12-03 13:55:27 [4,715,030ms] [Error] [omni.graph] Error executing python callback omni.graph.scriptnode.ScriptNode.release_instance 2024-12-03 13:55:27 [4,715,030ms] [Error] [omni.graph] Error executing python callback omni.graph.scriptnode.ScriptNode.release
Summary#
In this tutorial, you covered:
Occupancy map.
Running Isaac Sim with Nav2.
Running the Isaac ROS2 Navigation Goal package to send nav goals programmatically.
Running Waypoint Follower ActionGraph to send navigation goals.
Next Steps#
Continue on to the next tutorial in our ROS2 Tutorials series, Multiple Robot ROS2 Navigation to move multiple navigating robots with ROS2.
Further Learning#
To learn more about Nav2, refer to the project website.
More about Mapping.
Explore the inner workings of RTX Lidar sensors by learning Overview, and how to get RTX Sensor Annotators.