Articulation Controller#
Overview#
Articulation controller is the low level controller that controls joint position, joint velocity, and joint effort in Isaac Sim. The articulation controller can be interfaced using Python and Omnigraph.
Note
Angular units are expressed in radians while angles in USD are expressed in degrees and will be adjusted accordingly by the articulation controller.
Python Interface#
Create the articulation controller#
There are several ways to create the articulation controller. The articulation controller is usually created implicitly by applying articulation on a robot prim through the SingleArticulation class.
However, the articulation controller can be created directly by importing the controller class before the simulation starts, but this approach will require you to create or pass in the Articulation during initialization.
The snippet below will load and apply articulation on a franka robot.
1import isaacsim.core.utils.stage as stage_utils 2from isaacsim.core.prims import SingleArticulation 3usd_path = "/Path/To/Robots/FrankaRobotics/FrankaPanda/franka.usd" 4prim_path = "/World/envs/env_0/panda" 5 6# load the Franka Panda robot USD file 7stage_utils.add_reference_to_stage(usd_path, prim_path) 8# wrap the prim as an articulation 9prim = SingleArticulation(prim_path=prim_path, name="franka_panda")
1import isaacsim.core.utils.stage as stage_utils 2from isaacsim.core.api.controllers.articulation_controller import ArticulationController 3usd_path = "/Path/To/Robots/FrankaRobotics/FrankaPanda/franka.usd" 4prim_path = "/World/envs/env_0/panda" 5 6# load the Franka Panda robot USD file 7stage_utils.add_reference_to_stage(usd_path, prim_path) 8# Create the articulation controller 9articulation_controller = ArticulationController()
Initialize the controller#
After the simulation is started, the robot articulation must be initialized before any commands can be passed to the robot.
The more common approach is by initializing the single articulation object that you have created earlier, this will initialize the articulation controller and articulation view stored in the SingleArticulation object
1prim.initialize()
After the simulation starts, the articulation controller must be initialzied with an articulation view. Articulation view is the backend for selecting the joints and applying joint actions.
For example, the code snippet below creates an articulation view with the Franka robot and initializes the articulation controller.
1from isaacsim.core.prims import Articulation 2# Create the articulation view 3articulation_view = Articulation(prim_paths_expr="/World/envs/env_0/panda", name="franka_panda_view") 4# Initialize the articulation controller 5articulation_controller.initialize(articulation_view)
Articulation Action#
Joint controls commands are packaged in ArticulationAction objects first, before sending them to the articulation controller. The articulation controller allows you to specify the command joint postion, velocity and effort, as well as joint indicies of the joints actuated.
If the joint indice is empty, the articulation action will assume the command will apply to all joints of the robot, and if any of the command is 0, articulation action will assume it is unactuated.
For example, the snippet below creates the command that closes the franka robot fingers: panda_finger_joint1 (7) and panda_finger_joint2 (8) to 0.0
1import numpy as np
2from isaacsim.core.utils.types import ArticulationAction
3
4action = ArticulationAction(joint_positions=np.array([0.0, 0.0]), joint_indices=np.array([7, 8]))
This snippet creates the command that moves all the robot joints to the indicated position
1import numpy as np
2from isaacsim.core.utils.types import ArticulationAction
3
4action = ArticulationAction(joint_positions=np.array([0.0, -1.0, 0.0, -2.2, 0.0, 2.4, 0.8, 0.04, 0.04]))
Important
Make sure the joint commands matches the order and the number of joint indices passed in to the articulation action. If joint indice is not passed in, make sure the command matches the number of joints in the robot.
Note
A joint can only be controlled by one control method. For example a joint cannot be controlled by both desired position and desired torque
Apply Action#
The apply_action function in both SingleArticulation and ArticulationController classes will apply the ArticulationAction you created earlier to the robot.
1prim.apply_action(action)
1articulation_controller.apply_action(action)
Script Editor Example#
You can try out basic articulation controller examples by running the following code snippets in the Script Editor. For more advanced usage, it is recommended to follow the Core API Tutorial Series.
1import numpy as np 2from isaacsim.core.utils.stage import add_reference_to_stage 3from isaacsim.storage.native import get_assets_root_path 4from isaacsim.core.prims import SingleArticulation 5from isaacsim.core.utils.types import ArticulationAction 6from isaacsim.core.api.world import World 7import asyncio 8 9async def robot_control_example(): 10 if World.instance(): 11 World.instance().clear_instance() 12 world = World() 13 await world.initialize_simulation_context_async() 14 world.scene.add_default_ground_plane() 15 16 # Load the robot USD file 17 usd_path = get_assets_root_path() + "/Isaac/Robots/FrankaRobotics/FrankaPanda/franka.usd" 18 prim_path = "/World/envs/env_0/panda" 19 add_reference_to_stage(usd_path, prim_path) 20 21 # Create SingleArticulation wrapper (automatically creates articulation controller) 22 robot = SingleArticulation(prim_path=prim_path, name="franka_panda") 23 await world.reset_async() 24 25 # Initialize the robot (initializes articulation controller internally) 26 robot.initialize() 27 28 # Run simulation 29 await world.play_async() 30 31 # Get current joint positions 32 current_positions = robot.get_joint_positions() 33 print(f"Current joint positions: {current_positions}") 34 35 # Create target positions 36 target_positions = np.array([0.0, -1.5, 0.0, -2.8, 0.0, 2.8, 1.2, 0.04, 0.04]) 37 38 # Create and apply articulation action 39 action = ArticulationAction(joint_positions=target_positions) 40 robot.apply_action(action) 41 42 await asyncio.sleep(5.0) # Run for 5 seconds to reach target positions 43 44 # Get current joint positions 45 current_positions = robot.get_joint_positions() 46 print(f"Current joint positions: {current_positions}") 47 48 world.pause() 49 50# Run the example 51asyncio.ensure_future(robot_control_example())
1import numpy as np 2from isaacsim.core.utils.stage import add_reference_to_stage 3from isaacsim.storage.native import get_assets_root_path 4from isaacsim.core.api.controllers.articulation_controller import ArticulationController 5from isaacsim.core.prims import Articulation 6from isaacsim.core.utils.types import ArticulationAction 7from isaacsim.core.api.world import World 8import asyncio 9 10async def robot_control_example(): 11 if World.instance(): 12 World.instance().clear_instance() 13 world = World() 14 await world.initialize_simulation_context_async() 15 world.scene.add_default_ground_plane() 16 17 # Load the robot USD file 18 usd_path = get_assets_root_path() + "/Isaac/Robots/FrankaRobotics/FrankaPanda/franka.usd" 19 prim_path = "/World/envs/env_0/panda" 20 add_reference_to_stage(usd_path, prim_path) 21 22 # Create Articulation view for the robot 23 robot_view = Articulation(prim_paths_expr=prim_path, name="franka_panda_view") 24 25 # Create and initialize the articulation controller with the articulation view 26 articulation_controller = ArticulationController() 27 articulation_controller.initialize(robot_view) 28 29 # Run simulation 30 await world.play_async() 31 32 # Get current joint positions 33 current_positions = robot_view.get_joint_positions() 34 print(f"Current joint positions: {current_positions}") 35 36 # Create target positions 37 target_positions = np.array([0.0, -1.5, 0.0, -2.8, 0.0, 2.8, 1.2, 0.04, 0.04]) 38 39 # Create and apply articulation action 40 action = ArticulationAction(joint_positions=target_positions) 41 articulation_controller.apply_action(action) 42 43 await asyncio.sleep(5.0) # Run for 5 seconds to reach target positions 44 45 # Get current joint positions 46 current_positions = robot_view.get_joint_positions() 47 print(f"Current joint positions: {current_positions}") 48 49 world.pause() 50 51# Run the example 52asyncio.ensure_future(robot_control_example())
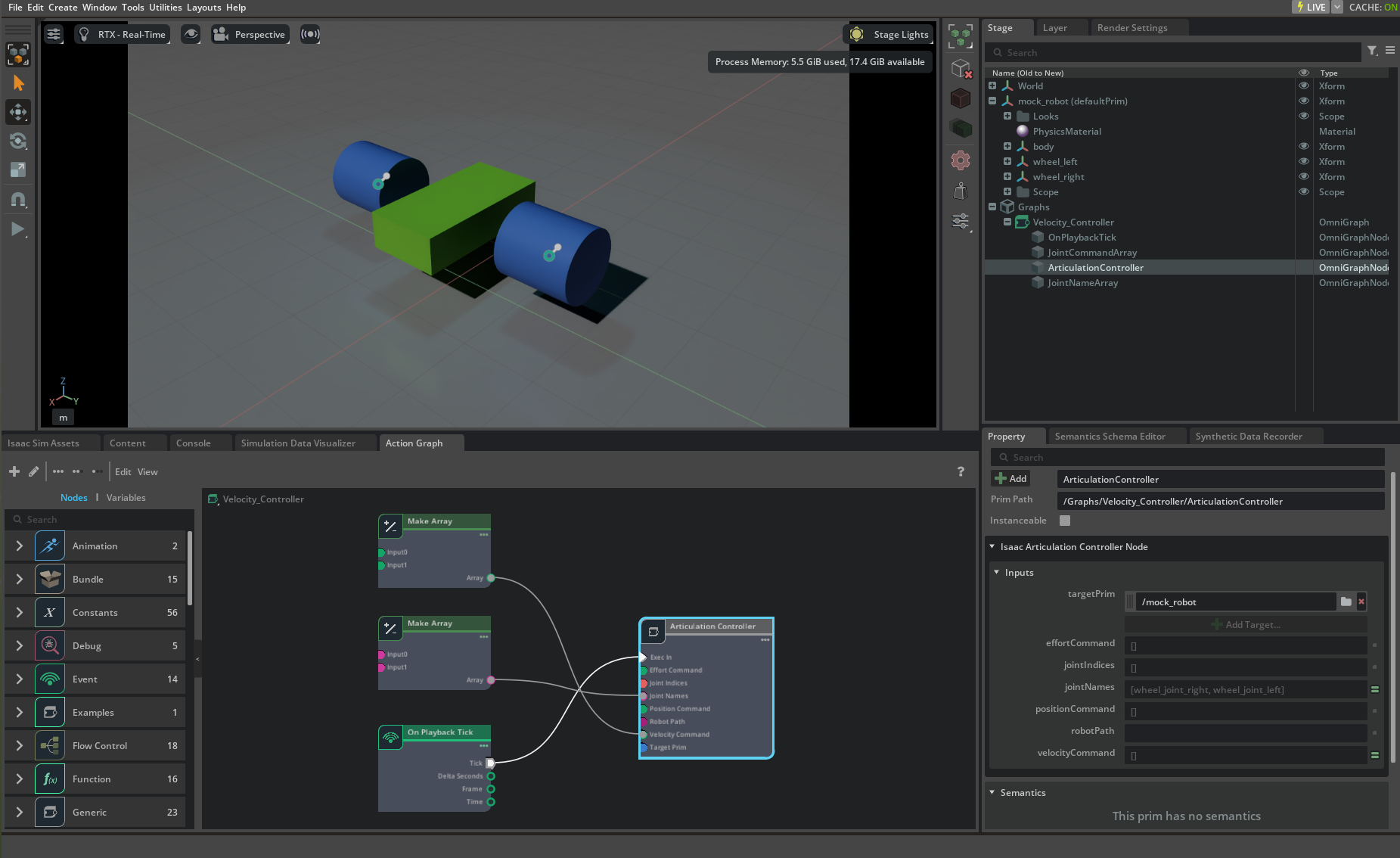
Omnigraph Interface#
The articulation controller can also be accessed through Omnigraph nodes, providing a visual, node-based approach to robot control.
Input Parameters#
The articulation controller Omnigraph node accepts the following input parameters:
Input Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
execIn |
Input execution trigger - connects to other nodes to control when the articulation controller runs |
targetPrim |
The prim containing the robot articulation root. Leave empty if using robotPath |
robotPath |
String path to the robot articulation root. Leave empty if using targetPrim |
jointIndices |
Array of joint indices to control. Leave empty to control all joints or use jointNames |
jointNames |
Array of joint names to control. Leave empty to control all joints or use jointIndices |
positionCommand |
Desired joint positions. Leave empty if not using position control |
velocityCommand |
Desired joint velocities. Leave empty if not using velocity control |
effortCommand |
Desired joint efforts/torques. Leave empty if not using effort control |
Usage Guidelines#
Important
Parameter Validation: Ensure joint commands match the order and number of joint indices or joint names. If neither joint indices nor joint names are specified, the command must match the total number of joints in the robot.
Note
Control Method Limitation: A joint can only be controlled by one method at a time. For example, a joint cannot be controlled by both position and effort commands simultaneously.
Example Usage#
For a complete example of the articulation controller Omnigraph node in action, see the mock_robot_rigged asset in the Content Browser at Isaac Sim > Samples > Rigging > MockRobot > mock_robot_rigged.usd.