Publishing Camera’s Data#
Learning Objectives#
In this tutorial, you learn how to programmatically set up publishers for Isaac Sim Cameras at an approximate frequency.
Getting Started#
Prerequisite
Completed the ROS 2 Cameras tutorial.
Completed ROS 2 Installation (Default) so that the necessary environment variables are set and sourced before launching NVIDIA Isaac Sim.
Read through the Sensor Axes Representation (LiDAR, Cameras).
Read through how to programmatically create a Camera sensor object in the scene.
ROS 2 Bridge is enabled.
Note
In Windows 10 or 11, depending on your machine’s configuration, RViz2 might not open properly.
Setup a Camera in a Scene#
To begin this tutorial, set up an environment with a isaacsim.sensors.camera Camera object. Running the following code results in a basic warehouse environment loaded with a camera in the scene.
1import carb
2from isaacsim import SimulationApp
3import sys
4
5BACKGROUND_STAGE_PATH = "/background"
6BACKGROUND_USD_PATH = "/Isaac/Environments/Simple_Warehouse/warehouse_with_forklifts.usd"
7
8CONFIG = {"renderer": "RayTracedLighting", "headless": False}
9
10# Example ROS 2 bridge sample demonstrating the manual loading of stages and manual publishing of images
11simulation_app = SimulationApp(CONFIG)
12import omni
13import numpy as np
14from isaacsim.core.api import SimulationContext
15from isaacsim.core.utils import stage, extensions
16from isaacsim.storage.native import get_assets_root_path
17import omni.graph.core as og
18import omni.replicator.core as rep
19import omni.syntheticdata._syntheticdata as sd
20
21from isaacsim.core.utils.prims import set_targets
22from isaacsim.sensors.camera import Camera
23import isaacsim.core.utils.numpy.rotations as rot_utils
24from isaacsim.core.utils.prims import is_prim_path_valid
25from isaacsim.core.nodes.scripts.utils import set_target_prims
26
27# Enable ROS 2 bridge extension
28extensions.enable_extension("isaacsim.ros2.bridge")
29
30simulation_app.update()
31
32simulation_context = SimulationContext(stage_units_in_meters=1.0)
33
34# Locate Isaac Sim assets folder to load environment and robot stages
35assets_root_path = get_assets_root_path()
36if assets_root_path is None:
37 carb.log_error("Could not find Isaac Sim assets folder")
38 simulation_app.close()
39 sys.exit()
40
41# Loading the environment
42stage.add_reference_to_stage(assets_root_path + BACKGROUND_USD_PATH, BACKGROUND_STAGE_PATH)
43
44
45###### Camera helper functions for setting up publishers. ########
46
47# Paste functions from the tutorial here
48# def publish_camera_tf(camera: Camera): ...
49# def publish_camera_info(camera: Camera, freq): ...
50# def publish_pointcloud_from_depth(camera: Camera, freq): ...
51# def publish_depth(camera: Camera, freq): ...
52# def publish_rgb(camera: Camera, freq): ...
53
54###################################################################
55
56# Create a Camera prim. The Camera class takes the position and orientation in the world axes convention.
57camera = Camera(
58 prim_path="/World/floating_camera",
59 position=np.array([-3.11, -1.87, 1.0]),
60 frequency=20,
61 resolution=(256, 256),
62 orientation=rot_utils.euler_angles_to_quats(np.array([0, 0, 0]), degrees=True),
63)
64camera.initialize()
65
66simulation_app.update()
67camera.initialize()
68
69############### Calling Camera publishing functions ###############
70
71# Call the publishers.
72# Make sure you pasted in the helper functions above, and uncomment out the following lines before running.
73
74approx_freq = 30
75#publish_camera_tf(camera)
76#publish_camera_info(camera, approx_freq)
77#publish_rgb(camera, approx_freq)
78#publish_depth(camera, approx_freq)
79#publish_pointcloud_from_depth(camera, approx_freq)
80
81####################################################################
82
83# Initialize physics
84simulation_context.initialize_physics()
85simulation_context.play()
86
87while simulation_app.is_running():
88 simulation_context.step(render=True)
89
90simulation_context.stop()
91simulation_app.close()
Publish Camera Intrinsics to CameraInfo Topic#
The following snippet will publish camera intrinsics associated with an isaacsim.sensors.camera Camera to a sensor_msgs/CameraInfo topic.
1def publish_camera_info(camera: Camera, freq): 2 from isaacsim.ros2.core import read_camera_info 3 # The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name. 4 render_product = camera._render_product_path 5 step_size = int(60/freq) 6 topic_name = camera.name+"_camera_info" 7 queue_size = 1 8 node_namespace = "" 9 frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing. 10 11 writer = rep.writers.get("ROS2PublishCameraInfo") 12 camera_info, _ = read_camera_info(render_product_path=render_product) 13 writer.initialize( 14 frameId=frame_id, 15 nodeNamespace=node_namespace, 16 queueSize=queue_size, 17 topicName=topic_name, 18 width=camera_info.width, 19 height=camera_info.height, 20 projectionType=camera_info.distortion_model, 21 k=camera_info.k.reshape([1, 9]), 22 r=camera_info.r.reshape([1, 9]), 23 p=camera_info.p.reshape([1, 12]), 24 physicalDistortionModel=camera_info.distortion_model, 25 physicalDistortionCoefficients=camera_info.d, 26 ) 27 writer.attach([render_product]) 28 29 gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path( 30 "PostProcessDispatch" + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product 31 ) 32 33 # Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate 34 og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size) 35 return
Publish Pointcloud from Depth Images#
In the following snippet, a pointcloud is published to a sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 message. This pointcloud is reconstructed from the depth image using the intrinsics of the camera.
1def publish_pointcloud_from_depth(camera: Camera, freq): 2 # The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name. 3 render_product = camera._render_product_path 4 step_size = int(60/freq) 5 topic_name = camera.name+"_pointcloud" # Set topic name to the camera's name 6 queue_size = 1 7 node_namespace = "" 8 frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing. 9 10 # Note, this pointcloud publisher will convert the Depth image to a pointcloud using the Camera intrinsics. 11 # This pointcloud generation method does not support semantic labeled objects. 12 rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar( 13 sd.SensorType.DistanceToImagePlane.name 14 ) 15 16 writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS2PublishPointCloud") 17 writer.initialize( 18 frameId=frame_id, 19 nodeNamespace=node_namespace, 20 queueSize=queue_size, 21 topicName=topic_name 22 ) 23 writer.attach([render_product]) 24 25 # Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate 26 gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path( 27 rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product 28 ) 29 og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size) 30 31 return
Publish RGB Images#
1def publish_rgb(camera: Camera, freq): 2 # The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name. 3 render_product = camera._render_product_path 4 step_size = int(60/freq) 5 topic_name = camera.name+"_rgb" 6 queue_size = 1 7 node_namespace = "" 8 frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing. 9 10 rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar(sd.SensorType.Rgb.name) 11 writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS2PublishImage") 12 writer.initialize( 13 frameId=frame_id, 14 nodeNamespace=node_namespace, 15 queueSize=queue_size, 16 topicName=topic_name 17 ) 18 writer.attach([render_product]) 19 20 # Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate 21 gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path( 22 rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product 23 ) 24 og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size) 25 26 return
Publish Depth Images#
1def publish_depth(camera: Camera, freq): 2 # The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name. 3 render_product = camera._render_product_path 4 step_size = int(60/freq) 5 topic_name = camera.name+"_depth" 6 queue_size = 1 7 node_namespace = "" 8 frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing. 9 10 rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar( 11 sd.SensorType.DistanceToImagePlane.name 12 ) 13 writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS2PublishImage") 14 writer.initialize( 15 frameId=frame_id, 16 nodeNamespace=node_namespace, 17 queueSize=queue_size, 18 topicName=topic_name 19 ) 20 writer.attach([render_product]) 21 22 # Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate 23 gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path( 24 rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product 25 ) 26 og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size) 27 28 return
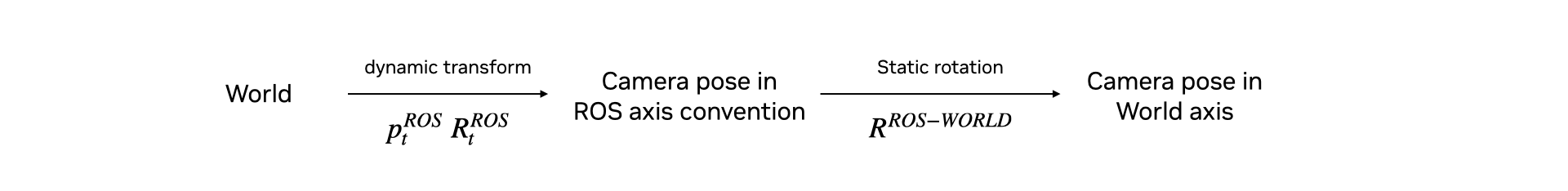
Publish a TF Tree for the Camera Pose#
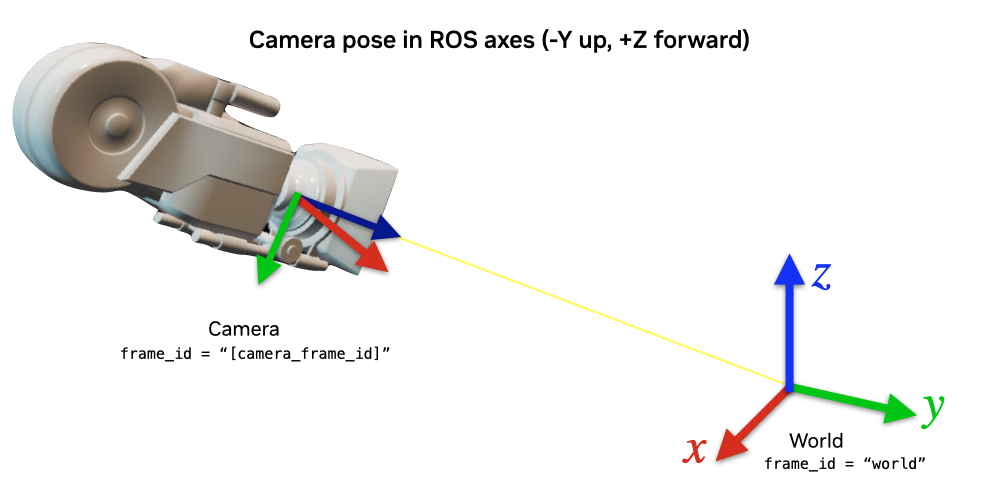
The pointcloud, published using the above function, will publish the pointcloud in the ROS camera axes convention (-Y up, +Z forward). To make visualizing this pointcloud easy in ROS using RViz, the following snippet will publish a TF Tree to the /tf, containing two frames.
The two frames are:
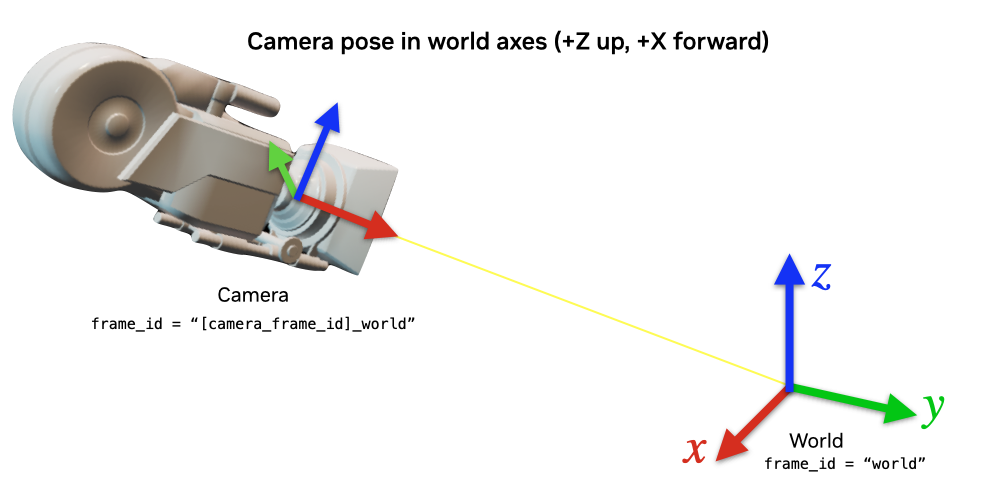
{camera_frame_id}: This is the camera’s pose in the ROS camera convention (-Y up, +Z forward). Pointclouds are published in this frame.{camera_frame_id}_world: This is the camera’s pose in the World axes convention (+Z up, +X forward). This will reflect the true pose of the camera.
The TF Tree looks like this:
world ->
{camera_frame_id}is a dynamic transform from origin to the camera in the ROS camera convention, following any movement of the camera.{camera_frame_id}->{camera_frame_id}_worldis a static transform consisting of only a rotation and zero translation. This static transform can be represented by the quaternion [0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5] in [w, x, y, z] convention.
Because the pointcloud is published in {camera_frame_id}, it is encouraged to set the frame_id of the pointcloud topic to {camera_frame_id}. The resulting visualization of the pointclouds can be viewed in the world frame in RViz.
1def publish_camera_tf(camera: Camera):
2 camera_prim = camera.prim_path
3
4 if not is_prim_path_valid(camera_prim):
5 raise ValueError(f"Camera path '{camera_prim}' is invalid.")
6
7 try:
8 # Generate the camera_frame_id. OmniActionGraph will use the last part of
9 # the full camera prim path as the frame name, so we will extract it here
10 # and use it for the pointcloud frame_id.
11 camera_frame_id=camera_prim.split("/")[-1]
12
13 # Generate an action graph associated with camera TF publishing.
14 ros_camera_graph_path = "/CameraTFActionGraph"
15
16 # If a camera graph is not found, create a new one.
17 if not is_prim_path_valid(ros_camera_graph_path):
18 (ros_camera_graph, _, _, _) = og.Controller.edit(
19 {
20 "graph_path": ros_camera_graph_path,
21 "evaluator_name": "execution",
22 "pipeline_stage": og.GraphPipelineStage.GRAPH_PIPELINE_STAGE_SIMULATION,
23 },
24 {
25 og.Controller.Keys.CREATE_NODES: [
26 ("OnTick", "omni.graph.action.OnTick"),
27 ("IsaacClock", "isaacsim.core.nodes.IsaacReadSimulationTime"),
28 ("RosPublisher", "isaacsim.ros2.bridge.ROS2PublishClock"),
29 ],
30 og.Controller.Keys.CONNECT: [
31 ("OnTick.outputs:tick", "RosPublisher.inputs:execIn"),
32 ("IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime", "RosPublisher.inputs:timeStamp"),
33 ]
34 }
35 )
36
37 # Generate 2 nodes associated with each camera: TF from world to ROS camera convention, and world frame.
38 og.Controller.edit(
39 ros_camera_graph_path,
40 {
41 og.Controller.Keys.CREATE_NODES: [
42 ("PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id, "isaacsim.ros2.bridge.ROS2PublishTransformTree"),
43 ("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world", "isaacsim.ros2.bridge.ROS2PublishRawTransformTree"),
44 ],
45 og.Controller.Keys.SET_VALUES: [
46 ("PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:topicName", "/tf"),
47 # Note if topic_name is changed to something else besides "/tf",
48 # it will not be captured by the ROS tf broadcaster.
49 ("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:topicName", "/tf"),
50 ("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:parentFrameId", camera_frame_id),
51 ("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:childFrameId", camera_frame_id+"_world"),
52 # Static transform from ROS camera convention to world (+Z up, +X forward) convention:
53 ("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:rotation", [0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5]),
54 ],
55 og.Controller.Keys.CONNECT: [
56 (ros_camera_graph_path+"/OnTick.outputs:tick",
57 "PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:execIn"),
58 (ros_camera_graph_path+"/OnTick.outputs:tick",
59 "PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:execIn"),
60 (ros_camera_graph_path+"/IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime",
61 "PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:timeStamp"),
62 (ros_camera_graph_path+"/IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime",
63 "PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:timeStamp"),
64 ],
65 },
66 )
67 except Exception as e:
68 print(e)
69
70 # Add target prims for the USD pose. All other frames are static.
71 set_target_prims(
72 primPath=ros_camera_graph_path+"/PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id,
73 inputName="inputs:targetPrims",
74 targetPrimPaths=[camera_prim],
75 )
76 return
Running the Example#
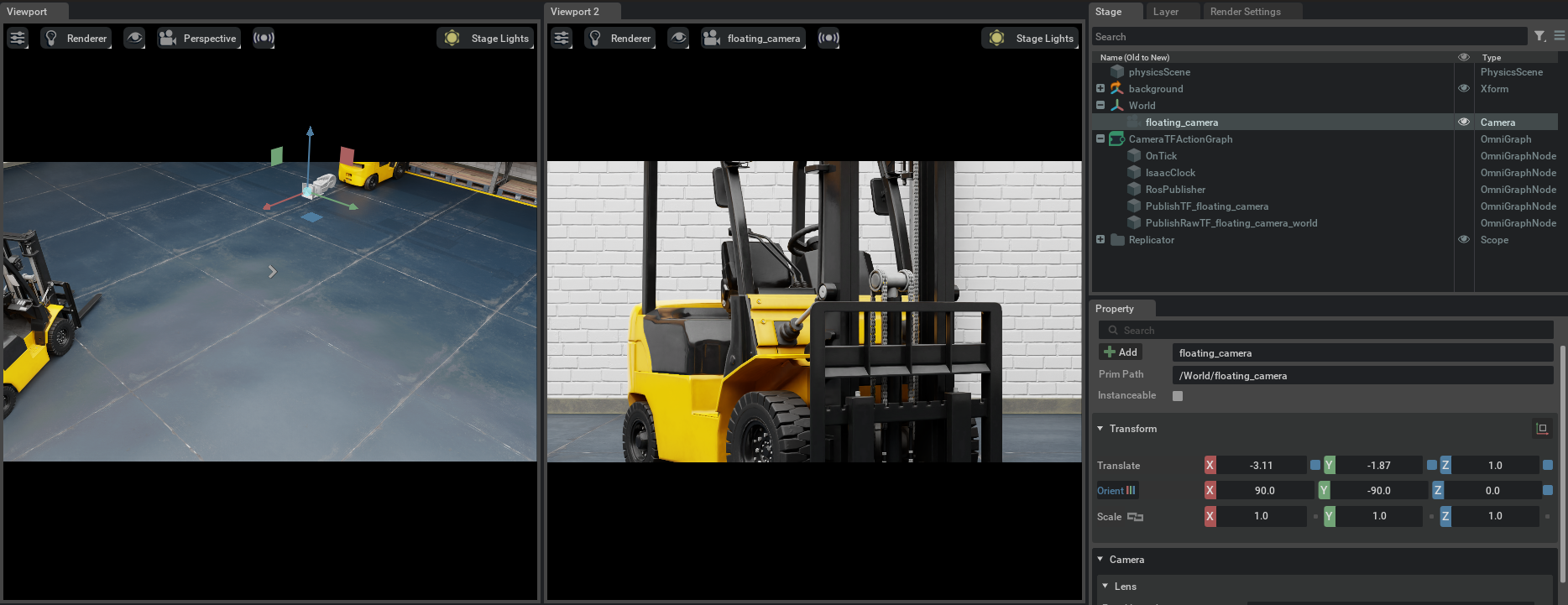
Enable isaacsim.ros2.bridge extension and set up ROS 2 environment variables following this workflow tutorial. Save the above script and run it using python.sh in the Isaac Sim folder. In our example, {camera_frame_id} is the prim name of the camera, which is floating_camera.
Verify that you observe a floating camera with prim path /World/floating_camera in the scene, and verify that the camera sees a forklift:
Verify that you observe the following:
If you open a terminal and type ros2 topic list, verify that you observe the following:
ros2 topic list
/camera_camera_info
/camera_depth
/camera_pointcloud
/camera_rgb
/clock
/parameter_events
/rosout
/tf
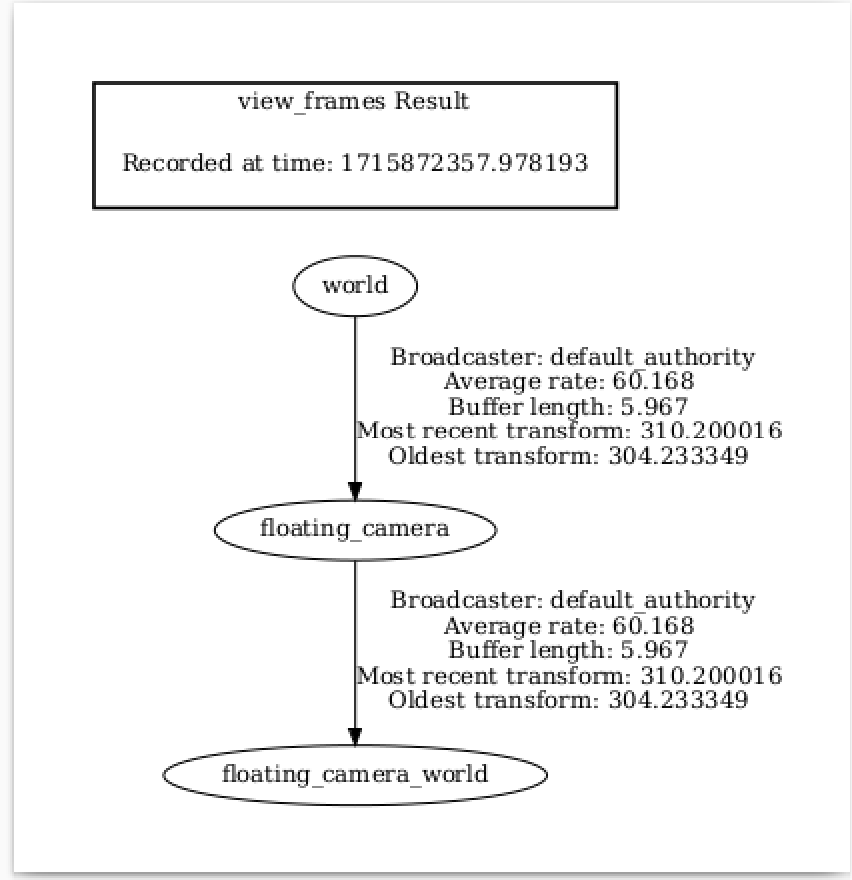
The frames published by TF will look like the following:
Now, you can visualize the pointcloud and depth images using RViz2. Open RViz2, and set the Fixed Frame field to world.
Then, enable viewing /camera_depth, /camera_rgb, /camera_pointcloud, and /tf topics.
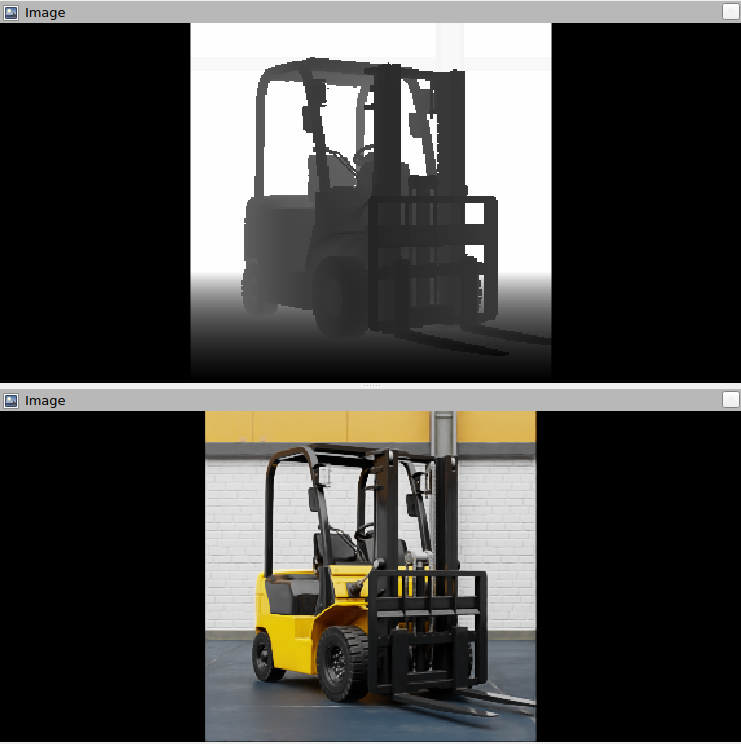
Verify that the depth image /camera_depth and RGB image /camera_rgb look like this:
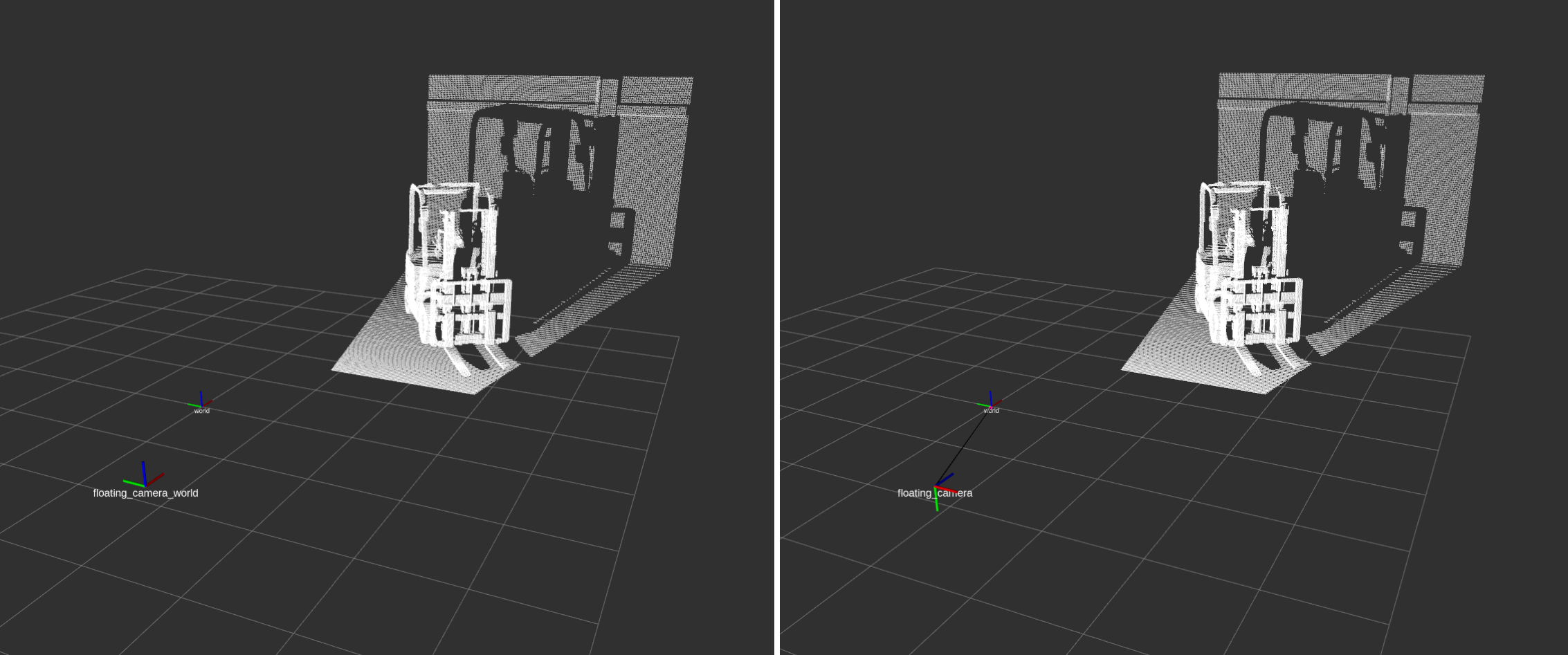
The pointcloud will look like so. Verify that the camera frames published by the TF publisher shows the two frames. The image on the left shows the {camera_frame_id}_world frame, and the image on the right shows the {camera_frame_id} frame.
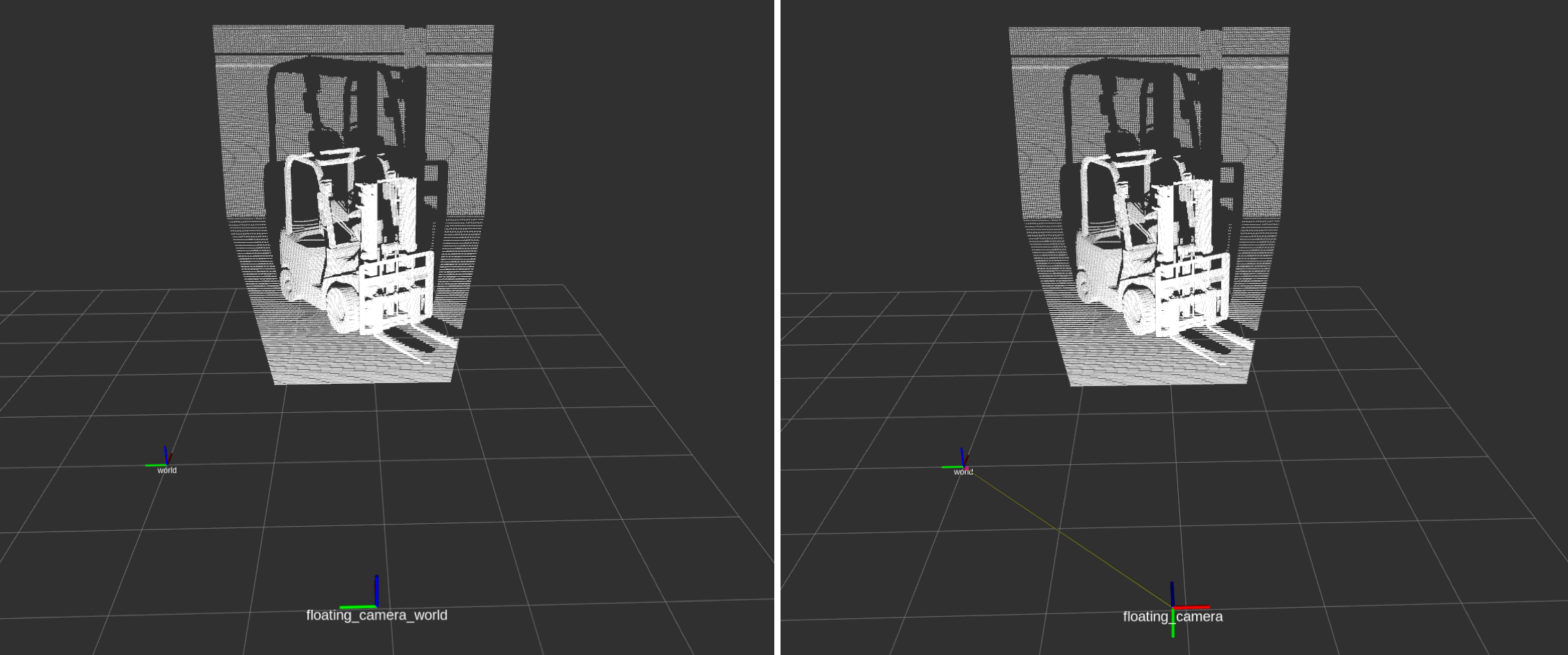
From the side view:
Summary#
This tutorial demonstrated how to programmatically set up ROS 2 publishers for Isaac Sim Cameras at an approximate frequency.
Next Steps#
Continue on to the next tutorial in our ROS 2 Tutorials series, RTX Lidar Sensors, to learn how to add a RTX Lidar sensor to the Turtlebot3.