9.9. Reinforcement Learning using Stable Baselines
9.9.1. Learning Objectives
This tutorial shows how to train a policy/ controller for Jetbot in Omniverse Isaac Sim to drive towards a random goal cube using its ground truth observations such as positions, orientations and velocities. After this tutorial, you can use stable baselines using custom environments in Omniverse Isaac Sim.
10-15 Minute Tutorial, Not Including Training time
9.9.2. Getting Started
Prerequisites
Review the Introductory Tutorial Series prior to beginning this tutorial.
9.9.3. The Environment
This is a simple environment to showcase how to use stable baselines with Omniverse Isaac Sim. The environment consists of a ground plane, Jetbot and a goal cube. The goal is to train a policy to drive the Jetbot to a random goal cube using its ground truth observations.
The action space is [forward_velocity, angular_velocity] for the Jetbot wheels.
The observation space is a 16 dim vector consiting of jetbot_world_position, jetbot_world_orientation, jetbot_linear_velocity, jetbot_angular_velocity and goal_world_position.
At the beginning of each episode (i.e.: on reset) the goal cube is randomized.
The reward is the difference between the previous distance to the goal before executing the current action and the current distance to the goal (i.e. is the Jetbot is getting closer or further to the goal?)
9.9.4. Train the Policy
Install dependencies in the isaac sim python environment
./python.sh -m pip install stable-baselines3 tensorboardTrain the policy by running the following script.
./python.sh standalone_examples/api/omni.isaac.jetbot/stable_baselines_example/train.pyLaunch tensorboard to look at how the policy training progresses.
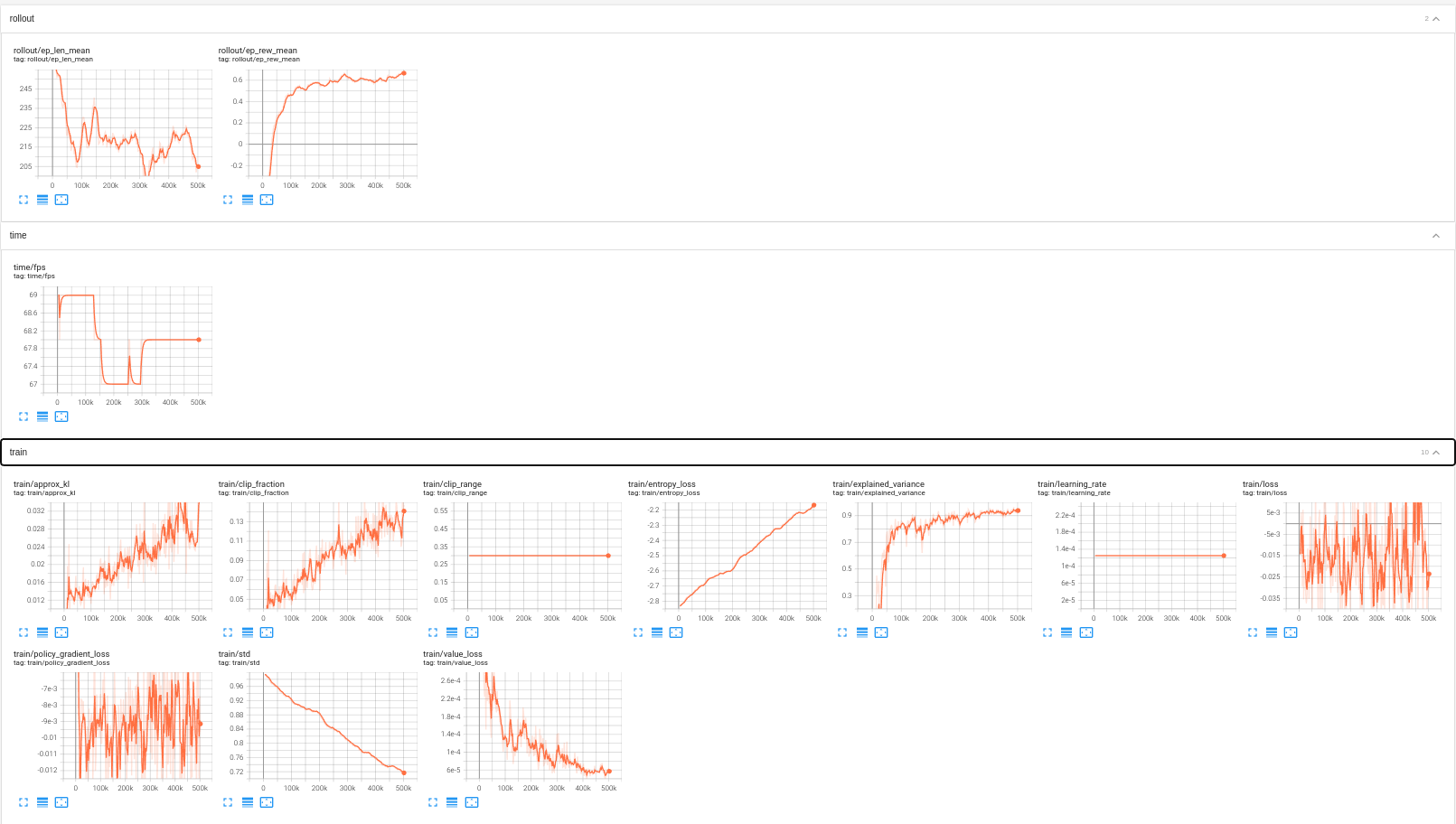
./python.sh .tensorboard --logdir ./
9.9.4.1. Code Overview
1from env import JetBotEnv
2from stable_baselines3 import PPO
3from stable_baselines3.ppo import CnnPolicy
4from stable_baselines3.common.callbacks import CheckpointCallback
5import torch as th
6
7# Log directory of the tensorboard files to visualize the training and for the final policy as well
8log_dir = "./cnn_policy"
9# set headles to False to visualize the policy while training
10my_env = JetBotEnv(headless=True)
11
12
13policy_kwargs = dict(activation_fn=th.nn.Tanh, net_arch=[16, dict(pi=[128, 128, 128], vf=[128, 128, 128])]) # Policy params
14policy = CnnPolicy
15total_timesteps = 500000
16
17# Saves a checkpoint policy in the same log directory
18checkpoint_callback = CheckpointCallback(save_freq=10000, save_path=log_dir, name_prefix="jetbot_policy_checkpoint")
19# PPO algorithm params
20model = PPO(
21 policy,
22 my_env,
23 policy_kwargs=policy_kwargs,
24 verbose=1,
25 n_steps=2560,
26 batch_size=64,
27 learning_rate=0.000125,
28 gamma=0.9,
29 ent_coef=7.5e-08,
30 clip_range=0.3,
31 n_epochs=5,
32 device="cuda",
33 gae_lambda=1.0,
34 max_grad_norm=0.9,
35 vf_coef=0.95,
36 max_grad_norm=10,
37 tensorboard_log=log_dir,
38)
39model.learn(total_timesteps=total_timesteps, callback=[checkpoint_callback])
40
41model.save(log_dir + "/jetbot_policy") # Saves the final policy
42
43my_env.close() # Closes the environment
9.9.5. Visualize the Trained Policy
Visualize the policy by running the following script
./python.sh standalone_examples/api/omni.isaac.jetbot/stable_baselines_example/eval.py
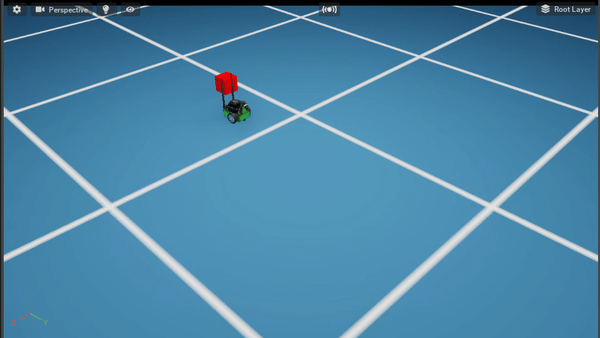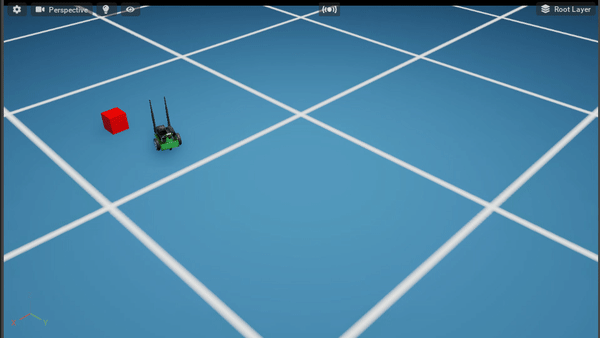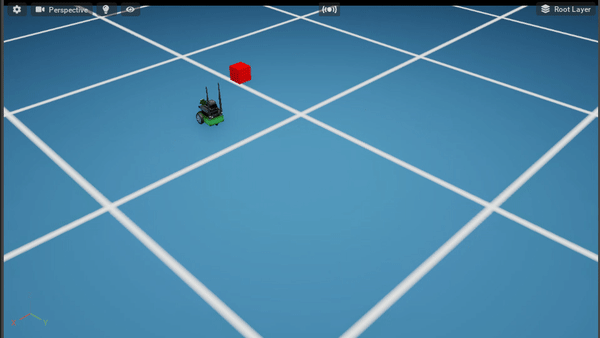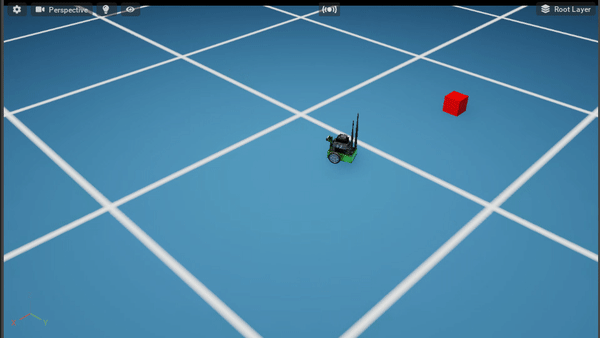
Policy After 100K steps
Policy After 300K steps
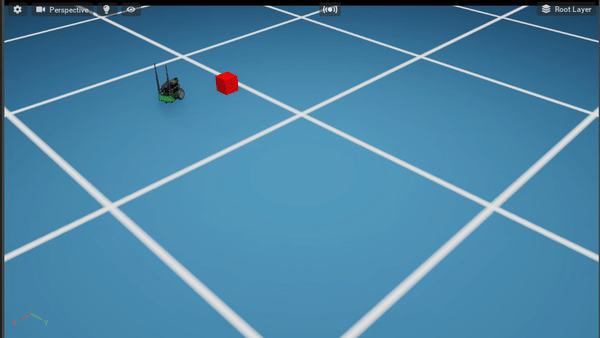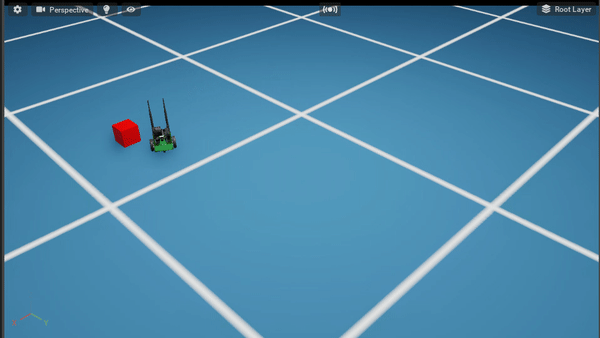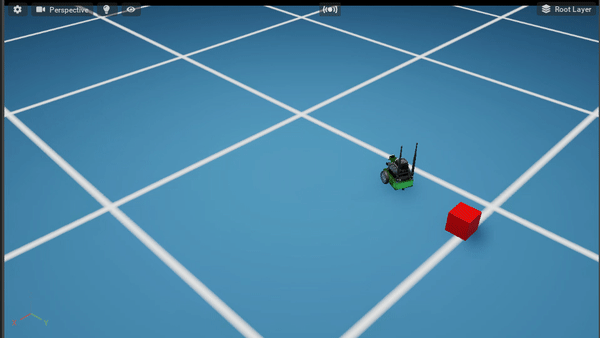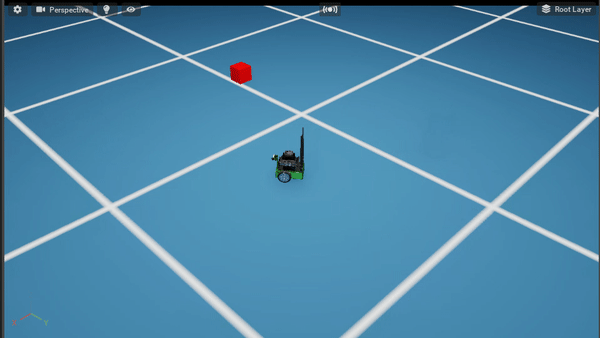
Policy After 500K steps
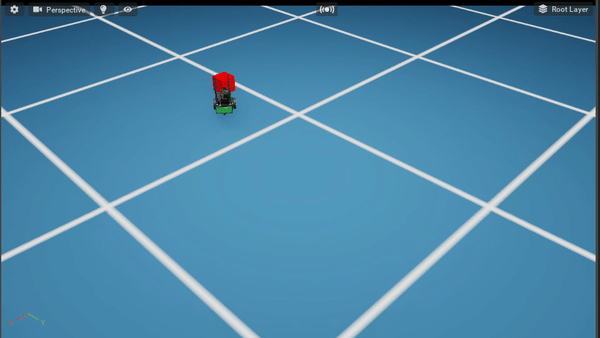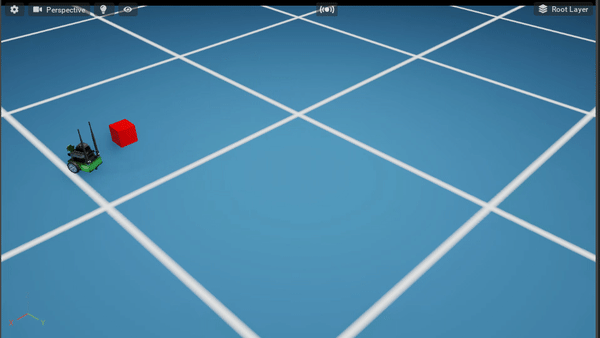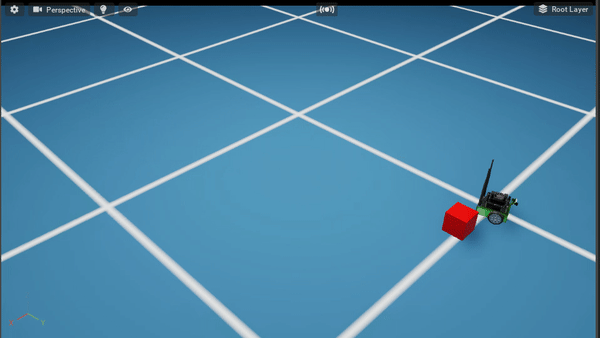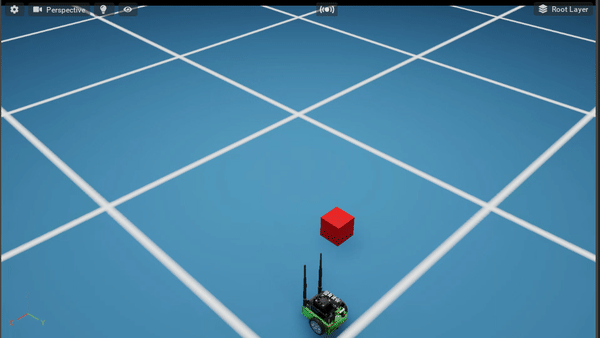
9.9.5.1. Code Overview
1from env import JetBotEnv
2from stable_baselines3 import PPO
3
4# Choose the policy path to visualize
5policy_path = "./cnn_policy/jetbot_policy.zip"
6
7my_env = JetBotEnv(headless=False)
8model = PPO.load(policy_path)
9
10for _ in range(20):
11 obs = my_env.reset()
12 done = False
13 while not done:
14 actions, _ = model.predict(observation=obs, deterministic=True)
15 obs, reward, done, info = my_env.step(actions)
16 my_env.render()
17
18my_env.close()
9.9.6. Create a Custom Environment
Have a look at the environment code at standalone_examples/api/omni.isaac.jetbot/stable_baselines_example/env.py to create similar environments.
1import gym
2from gym import spaces
3import numpy as np
4import math
5import carb
6
7
8class JetBotEnv(gym.Env):
9 metadata = {"render.modes": ["human"]}
10
11 def __init__(
12 self,
13 skip_frame=1,
14 physics_dt=1.0 / 60.0,
15 rendering_dt=1.0 / 60.0,
16 max_episode_length=256,
17 seed=0,
18 headless=True,
19 ) -> None:
20 from omni.isaac.kit import SimulationApp
21
22 self.headless = headless
23 self._simulation_app = SimulationApp({"headless": self.headless, "anti_aliasing": 0})
24 self._skip_frame = skip_frame
25 self._dt = physics_dt * self._skip_frame
26 self._max_episode_length = max_episode_length
27 self._steps_after_reset = int(rendering_dt / physics_dt)
28 from omni.isaac.core import World
29 from omni.isaac.wheeled_robots.robots import WheeledRobot
30 from omni.isaac.wheeled_robots.controllers.differential_controller import DifferentialController
31 from omni.isaac.core.objects import VisualCuboid
32 from omni.isaac.core.utils.nucleus import get_assets_root_path
33
34 self._my_world = World(physics_dt=physics_dt, rendering_dt=rendering_dt, stage_units_in_meters=1.0)
35 self._my_world.scene.add_default_ground_plane()
36 assets_root_path = get_assets_root_path()
37 if assets_root_path is None:
38 carb.log_error("Could not find Isaac Sim assets folder")
39 return
40 jetbot_asset_path = assets_root_path + "/Isaac/Robots/Jetbot/jetbot.usd"
41 self.jetbot = self._my_world.scene.add(
42 WheeledRobot(
43 prim_path="/jetbot",
44 name="my_jetbot",
45 wheel_dof_names=["left_wheel_joint", "right_wheel_joint"],
46 create_robot=True,
47 usd_path=jetbot_asset_path,
48 position=np.array([0, 0.0, 0.03]),
49 orientation=np.array([1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
50 )
51 )
52 self.jetbot_controller = DifferentialController(name="simple_control", wheel_radius=0.0325, wheel_base=0.1125)
53 self.goal = self._my_world.scene.add(
54 VisualCuboid(
55 prim_path="/new_cube_1",
56 name="visual_cube",
57 position=np.array([0.60, 0.30, 0.05]),
58 size=0.1,
59 color=np.array([1.0, 0, 0]),
60 )
61 )
62 self.seed(seed)
63 self.reward_range = (-float("inf"), float("inf"))
64 gym.Env.__init__(self)
65 self.action_space = spaces.Box(low=-1, high=1.0, shape=(2,), dtype=np.float32)
66 self.observation_space = spaces.Box(low=float("inf"), high=float("inf"), shape=(16,), dtype=np.float32)
67
68 self.max_velocity = 1
69 self.max_angular_velocity = math.pi
70 self.reset_counter = 0
71 return
72
73 def get_dt(self):
74 return self._dt
75
76 def step(self, action):
77 previous_jetbot_position, _ = self.jetbot.get_world_pose()
78 # action forward velocity , angular velocity on [-1, 1]
79 raw_forward = action[0]
80 raw_angular = action[1]
81
82 # we want to force the jetbot to always drive forward
83 # so we transform to [0,1]. we also scale by our max velocity
84 forward = (raw_forward + 1.0) / 2.0
85 forward_velocity = forward * self.max_velocity
86
87 # we scale the angular, but leave it on [-1,1] so the
88 # jetbot can remain an ambiturner.
89 angular_velocity = raw_angular * self.max_angular_velocity
90
91 # we apply our actions to the jetbot
92 for i in range(self._skip_frame):
93 self.jetbot.apply_wheel_actions(
94 self.jetbot_controller.forward(command=[forward_velocity, angular_velocity])
95 )
96 self._my_world.step(render=False)
97
98 observations = self.get_observations()
99 info = {}
100 done = False
101 if self._my_world.current_time_step_index - self._steps_after_reset >= self._max_episode_length:
102 done = True
103 goal_world_position, _ = self.goal.get_world_pose()
104 current_jetbot_position, _ = self.jetbot.get_world_pose()
105 previous_dist_to_goal = np.linalg.norm(goal_world_position - previous_jetbot_position)
106 current_dist_to_goal = np.linalg.norm(goal_world_position - current_jetbot_position)
107 reward = previous_dist_to_goal - current_dist_to_goal
108 if current_dist_to_goal < 0.1:
109 done = True
110 return observations, reward, done, info
111
112 def reset(self):
113 self._my_world.reset()
114 self.reset_counter = 0
115 # randomize goal location in circle around robot
116 alpha = 2 * math.pi * np.random.rand()
117 r = 1.00 * math.sqrt(np.random.rand()) + 0.20
118 self.goal.set_world_pose(np.array([math.sin(alpha) * r, math.cos(alpha) * r, 0.05]))
119 observations = self.get_observations()
120 return observations
121
122 def get_observations(self):
123 self._my_world.render()
124 jetbot_world_position, jetbot_world_orientation = self.jetbot.get_world_pose()
125 jetbot_linear_velocity = self.jetbot.get_linear_velocity()
126 jetbot_angular_velocity = self.jetbot.get_angular_velocity()
127 goal_world_position, _ = self.goal.get_world_pose()
128 return np.concatenate(
129 [
130 jetbot_world_position,
131 jetbot_world_orientation,
132 jetbot_linear_velocity,
133 jetbot_angular_velocity,
134 goal_world_position,
135 ]
136 )
137
138 def render(self, mode="human"):
139 return
140
141 def close(self):
142 self._simulation_app.close()
143 return
144
145 def seed(self, seed=None):
146 self.np_random, seed = gym.utils.seeding.np_random(seed)
147 np.random.seed(seed)
148 return [seed]
9.9.7. Summary
This tutorial covered the following topics:
Using stable baselines with Isaac Sim.
Training a PPO policy for jetbot to drive to a random cube.
Visualizing a trained policy.
Launching a tensorboard to visualize the training progress.